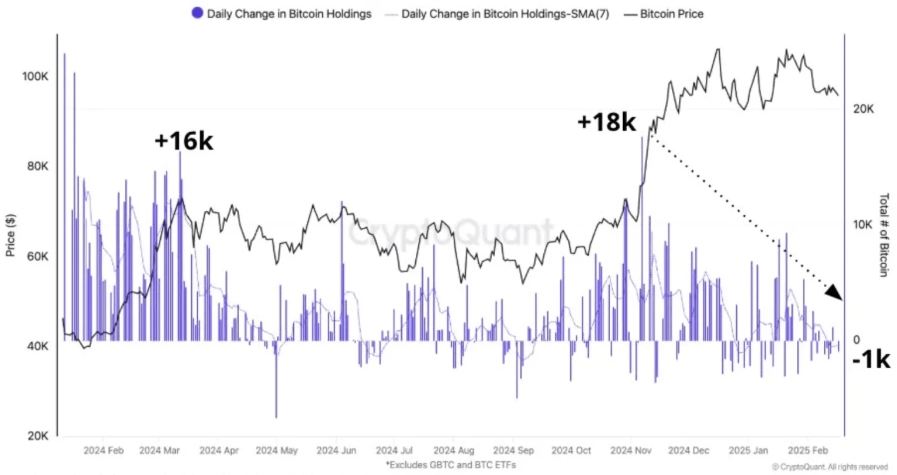
Central banks around the world are exploring how tokenization can enhance the management of foreign exchange (FX) reserves. Traditionally held in the form of government bonds, foreign currencies, and gold, these reserves serve as the foundation of a nation’s monetary stability. However, in an era of digital transformation, tokenized FX reserves are emerging as a next-generation tool for improving liquidity, transparency, and risk management in global finance.
Tokenization allows reserve assets to exist as secure, programmable digital tokens on regulated distributed ledger systems. This innovation is redefining how central banks manage cross-border liquidity, settle payments, and conduct monetary operations. By digitizing reserves, central banks can achieve faster settlements, optimize collateral allocation, and gain real-time insight into global liquidity flows.
Reimagining Reserve Management Through Tokenization
FX reserves have long been a cornerstone of financial stability, but managing them involves complex coordination between institutions, custodians, and markets. Settlement delays, high transaction costs, and limited interoperability often reduce the efficiency of reserve deployment. Tokenization addresses these challenges by creating a shared infrastructure where assets can move securely across jurisdictions with minimal friction.
Through tokenized platforms, central banks can hold and transfer digital representations of major reserve assets such as U.S. Treasuries, euro-denominated bonds, or gold-backed instruments on interoperable ledgers. Smart contracts can automate key functions such as collateral management, interest payments, and foreign exchange swaps, reducing operational bottlenecks.
Early experiments, including projects led by the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and several central banks in Asia and Europe, demonstrate that tokenized FX reserves can settle instantaneously while maintaining full regulatory oversight. These pilots show that integrating tokenized reserves into cross-border payment systems could eliminate settlement risk and improve liquidity distribution during periods of market stress.
The technology also supports more dynamic portfolio management. Central banks can reallocate assets in real time based on market conditions, risk metrics, or policy objectives. By leveraging tokenized reserves, monetary authorities can respond more quickly to liquidity shortages, exchange rate fluctuations, or financial contagion across borders.
Institutional Adoption and Interoperable Infrastructure
The shift toward tokenized reserves is not isolated it is part of a broader trend toward digital monetary systems. Several central banks are now exploring how tokenized reserves can interoperate with central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) and tokenized sovereign bonds.
For instance, a tokenized U.S. Treasury could be used as collateral in an interbank transaction settled via a CBDC or stablecoin. This interoperability would enable near-instant cross-currency swaps, reducing the need for correspondent banking networks. Such functionality could transform how institutions manage global liquidity, making monetary policy transmission more efficient and responsive.
Institutional custodians, global payment networks, and asset managers are increasingly participating in these initiatives. Regulated digital custody providers now offer infrastructure capable of holding tokenized sovereign assets in compliance with global standards such as ISO 20022 and Basel III. These systems integrate directly with on-chain governance and reporting mechanisms, ensuring transparency and auditability for policymakers and regulators.
The benefits extend beyond efficiency. Tokenized reserves could strengthen financial inclusion for smaller nations with limited access to global liquidity channels. By connecting to tokenized reserve networks, these countries could engage directly in digital foreign exchange operations without relying on intermediaries. This innovation has the potential to democratize access to global capital markets while maintaining institutional-grade security.
However, the success of tokenized reserves depends on standardization and interoperability. Without global coordination, fragmented systems could create new forms of financial risk. To address this, the BIS and other international bodies are working to define shared protocols and legal standards that ensure tokenized reserves are recognized across borders.
Regulation, Transparency, and Global Cooperation
Policymakers are aware that tokenizing FX reserves introduces both opportunities and responsibilities. Legal frameworks must define ownership rights, settlement finality, and data governance in multi-jurisdictional contexts.
The IMF and Financial Stability Board have emphasized that tokenized reserve assets must be backed by clear legal recognition, transparent audit mechanisms, and robust cybersecurity safeguards. Several jurisdictions are now developing pilot regulations to test how tokenized sovereign assets can integrate with national accounting standards.
Transparency is also a major benefit. Tokenized reserves can offer real-time visibility into a country’s holdings, creating new levels of accountability for both central banks and international institutions. Smart contracts can automatically generate compliance reports, reducing manual oversight and improving policy coordination among financial authorities.
The growing interest in tokenized reserves is fostering collaboration among central banks from both developed and emerging economies. Joint initiatives between BRICS nations and European regulators are exploring how tokenized FX reserves could enhance financial stability and cross-border liquidity management. These partnerships represent an important step toward a globally connected, digitally governed monetary system.
Conclusion
Tokenized FX reserves are redefining how central banks approach liquidity, transparency, and efficiency. By integrating blockchain technology into the management of sovereign assets, monetary authorities can modernize their operations while preserving the trust and security that underpin the global financial system. As pilot programs expand and regulatory frameworks mature, tokenized reserves could become a cornerstone of the next generation of central banking. The future of liquidity management will not only be digital it will be programmable, interoperable, and global.